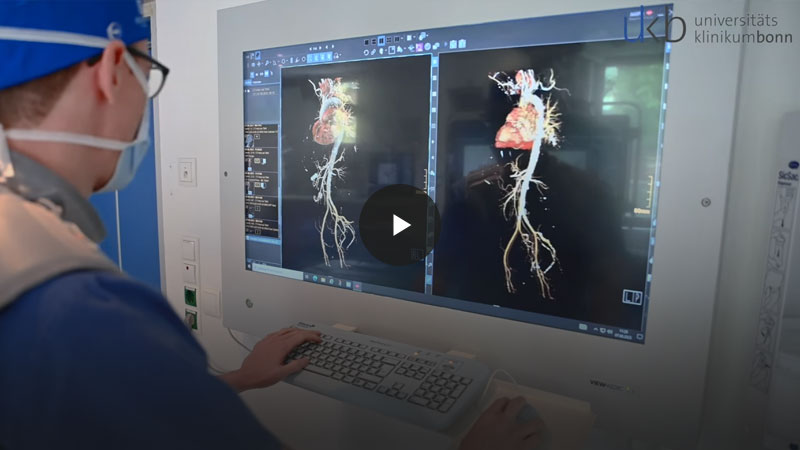
AI integration in diagnosis and therapy
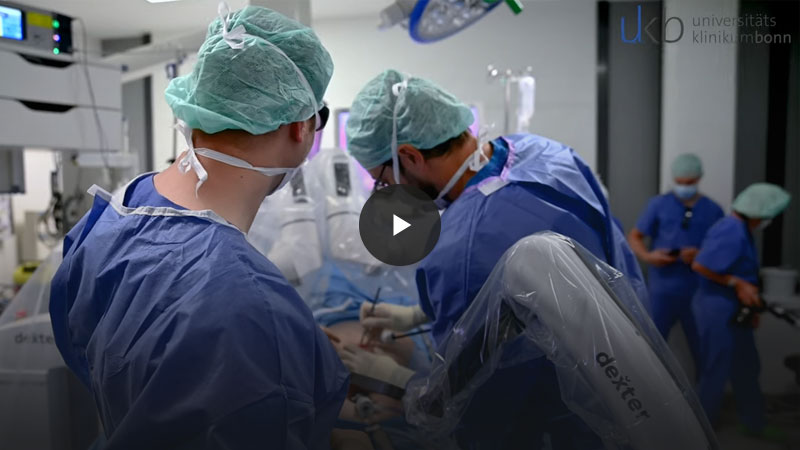
Robotics in surgery
As part of the ISMC, the UKB was one of the first hospitals in Germany to introduce the innovative robotic surgical system "Dexter". The system, which is already in clinical use at the UKB, follows the approach of "on-demand robotics", i.e. the demand-oriented use of the surgical robot for surgical steps in which robotic technology is advantageous.
It has a modular design and can be combined technically and logistically with conventional minimally invasive surgical procedures (keyhole surgery). A particular advantage is that the surgeon at the console is sterile and can easily go to the patient at the operating table. In acute emergency situations, this can provide valuable time for increased patient safety.
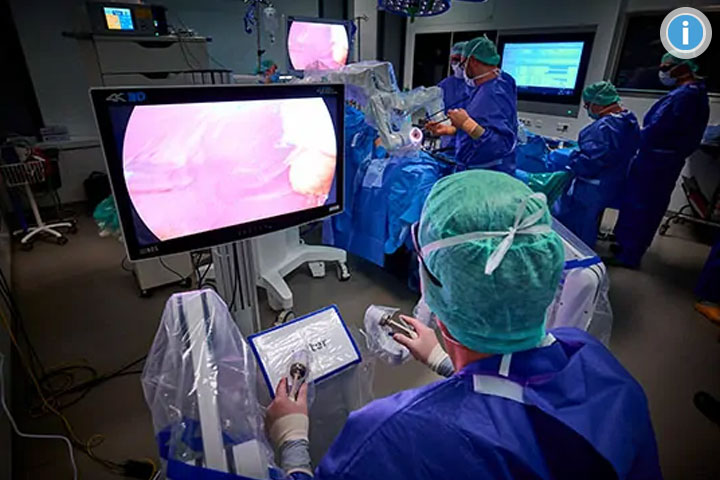

Robotics in diagnostic radiology:
As part of the ISMC, innovative systems for endovascular robotics are being established and further developed so that interventional procedures can already be carried out robotically at the UKB. The further development enables "remote" control by the treating interventionalist, so that the intervention can be carried out from the so-called control room using a joystick.
The attending physician does not need to wear lead protection and is not exposed to radiation in the control room, which significantly reduces radiation exposure. In addition, the robot technology enables precise catheter control, medication application and positioning of devices, so that interventional procedures can ultimately be carried out more precisely.
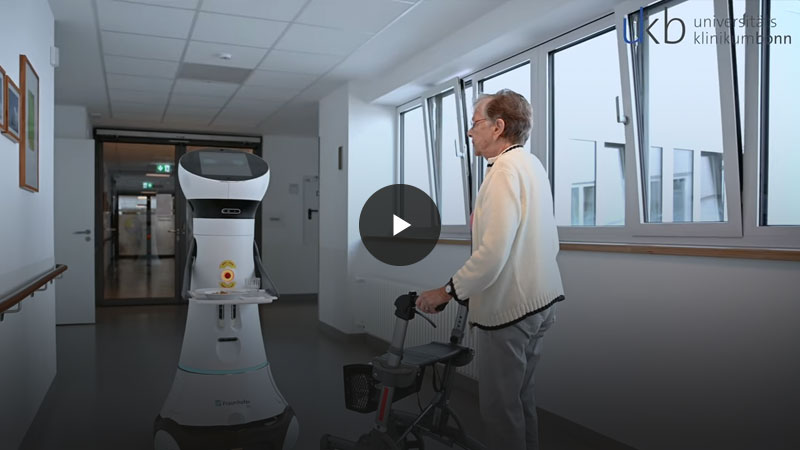
Care robotics
The ISMC sub-project aims to digitize and simplify care processes. By leveraging robotics and digital devices, the project seeks to alleviate the burden on nursing staff in the long term. Additionally, we are enhancing training formats through an innovative virtual reality (VR) training environment, which provides new learning experiences and makes training more engaging.
Here are two specific examples:
The ongoing ISMC project involves the development of care robots specifically designed for nutritional care. An interdisciplinary team of nursing and nutritional scientists collaborates with other scientific institutions to create applicable concepts that support nursing staff in administering food and drinks. Accordingly, the robots can deliver trays of food and serve beverages. Built-in scanners allow precise recording of food and drink quantities, enabling quick intervention in case of deviations. Intelligent devices, such as cups with colour scales or voice output, also encourage patients to stay hydrated.
Currently, a novel training environment is being developed within the UKB’s Centre for Education and Training (CAW) in the metaverse. In this virtual environment, specific nursing scenarios are simulated, allowing trainees to practice nursing procedures, interact with patients and their surroundings, and enhance professional decision-making skills.
The project also aims to extend the developed educational content to international partner universities and vocational schools. This contributes to standardizing the quality of education and simultaneously supports international educational collaborations.
The virtual training environment is controlled through VR headsets. Its simple and intuitive operation using hand gestures ensures user-friendliness, even for first-time users. By considering potential developments early on (such as AI applications or integrating a chatbot function) and providing relevant interfaces, the context relevance is strengthened, and future needs are addressed.
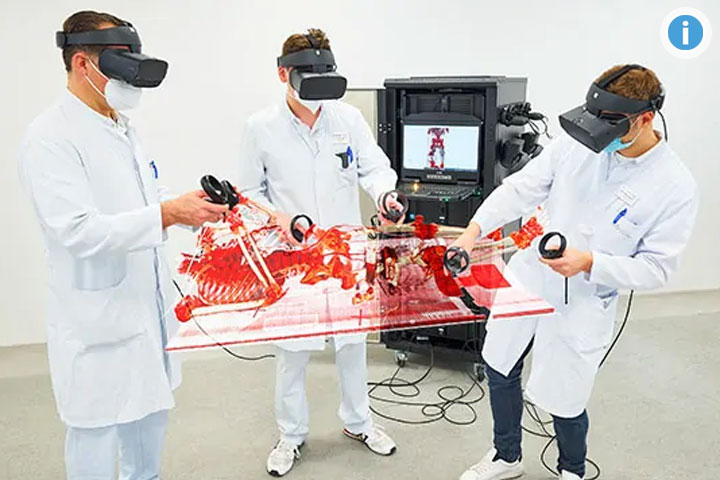
Medicine in mixed reality
A completely new surgical and medical metaverse is currently being created at the UKB as part of the ISMC. The planning of surgical procedures, their navigation, interdisciplinary case discussions (e.g. tumor boards) and the digital integration of the patient into the treatment pathway are to take place collaboratively and immersively in virtual space. For this purpose, an on-campus hosted visualization cloud was set up as a computing and data provider for XR (extended reality) end devices such as VR (virtual reality) glasses.
In this medical metaverse, patient data, in particular imaging, is displayed three-dimensionally and can be viewed, processed and discussed together regardless of the user's location. Operation is as simple as it is intuitive using hand gestures and is also quickly learned by first-time users. In the future, AI applications will also be integrated into this environment to further develop the visualization.

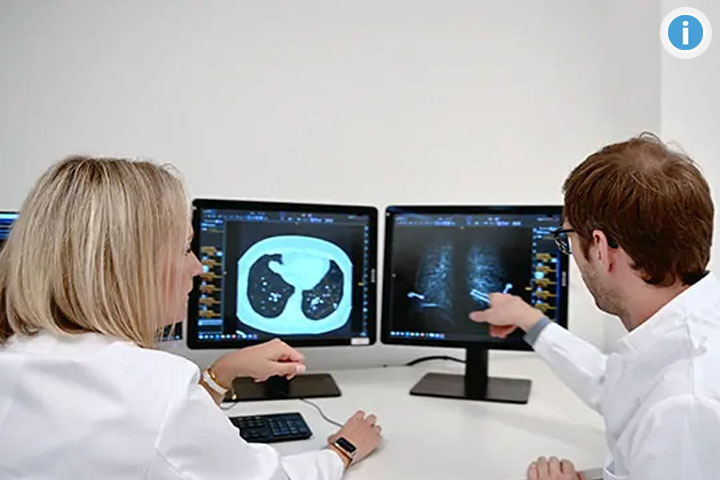
Clinical Decision Support Systeme
AI processes make it possible to take clinical decision support systems to a new level - from automatic alerts based on the data situation to therapy recommendations. The ISMC is testing and further developing AI-based procedures. To this end, the IT architecture has been adapted for the use and further development of AI-based decision support systems.
With the AI-RAD Companion, models for the diagnosis of the prostate and liver are already being used in a research context at the UKB. In the future, doctors should be able to save important time in the diagnostic process with the help of AI models.