AG Kato
Luca, D., Lee, S., Hirota, K., Okabe, Y., Uehori, J., Izawa, K., Lanz, A.-L., Schütte, V., Sivri, B., Tsukamoto, Y., Hauck, F., Behrendt, R., Roers, A., Fujita, T., Nishikomori, R., Lee-Kirsch, M.A., and Kato, H. (2024). Aberrant RNA sensing in regulatory T cells causes systemic autoimmunity. Science advances 10, eadk0820. ♦
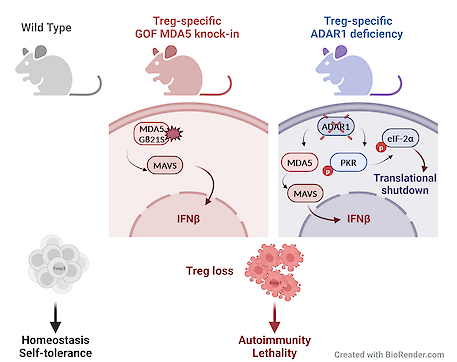
Fig. Constitutive MDA5 signaling, and ADAR1 deficiency causes aberrant downstream activation of innate immune sensors MDA5 and PKR, disturbs Treg homeostasis in mice, resulting in severe autoimmunity and lethality
© Image (created with BioRender.com): Domnica Luca/UKB
Tsukamoto, Y., Igarashi, M., Kato, H.*. (2023). Targeting cap1 RNA methyltransferases as an antiviral strategy. Cell Chemical Biology. ♦
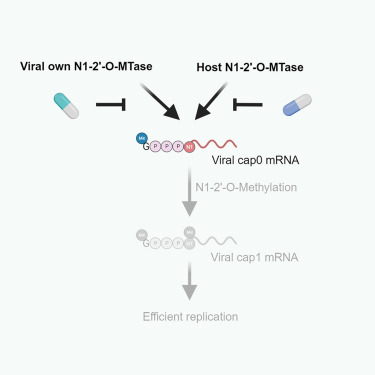
In this review, Tsukamoto et al. focus on the importance of the presence of N1-2′-O-Me in viral RNAs and discuss the potential for drug development by targeting host and viral N1-2′-O-methyltransferases.
© Image: Tsukamoto et al., Graphical abstract
Im JH, Duic I, Yoshimura SH, Onomoto K, Yoneyama M, Kato H, Fujita T. Mechanisms of length-dependent recognition of viral double-stranded RNA by RIG-I. Sci Rep. 2023 Apr 18;13(1):6318. doi: 10.1038/s41598-023-33208-w.PMID: 37072508 ♦
Tsukamoto, Y., Hiono, T., Yamada, S., Matsuno, K., Faist, A., Claff, T., Hou, J., Namasivayam, V., vom Hemdt, A., Sugimoto, S., Ng, Y.J., Christensen, M.H., Tesfamariam, Y.M., Wolter, S., Juranek, S., Zillinger, T., Bauer, S., Hirokawa, T., Schmidt, F.I., Kochs, G., Shimojima, M., Huang, Y-S., Pichlmair, A., Kümmerer, B.M., Sakoda, Y., Schlee, M., Brunotte, L., Müller, C.E., Igarashi, M.*, Kato, H.*. (2023). Inhibition of cellular RNA methyltransferase abrogates influenza virus capping and replication. Science 379. ♦
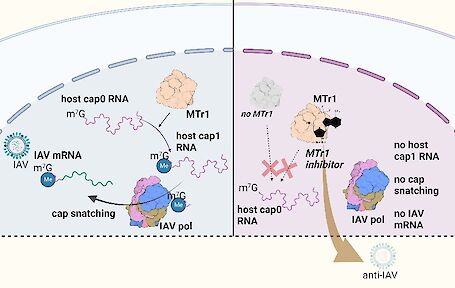
IAV replication in the presence or absence of MTr1: - The host RNA is methylated by MTr1 to a mature cap1 RNA. The influenza virus snatches the cap part of the mature host RNA to start viral replication. MTr1-deficient cells or cells treated with MTr1 inhibitors do not lead to IAV replication.
© Image (created with BioRender.com): Yuta Tsukamoto/UKB
Kira A, Tatsutomi I, Saito K, Murata M, Hattori I, Kajita H, Muraki N, Oda Y, Satoh S, Tsukamoto Y, Kimura S, Kato H, Hirashima T, Kawane K. Extracellular vesicle formation mediated by local phosphatidylserine exposure promotes efficient cell extrusion. EPMC. preprint 2023 Mar 02. doi: 10.21203/rs.3.rs-257262/v2 ♦
Schumann, T., Ramon, S.C., Schubert, N., Mayo, M.A., Hega, M., Maser, K.I., Ada, S.-R., Sydow, L., Hajikazemi, M., Badstübner, M., Müller, P., Ge, Y., Shakeri, F., Buness, A., Rupf, B., Lienenklaus, S., Utess, B., Muhandes, L., Haase, M., Rupp, L., Schmitz, M., Gramberg, T., Manel, N., Hartmann, G., Zillinger, T., Kato, H., Bauer, S., Gerbaulet, A., Paeschke, K., Roers, A., and Behrendt, R. (2023). Deficiency for SAMHD1 activates MDA5 in a cGAS/STING-dependent manner. The Journal of experimental medicine 220. ♦
Kikuchi, M., Kadena, M., Fukamachi, H., Takaki, T., Matsui, S., Hoashi-Takiguchi, S., Morisaki, H., Trtić, N., Mori, M., Kurosawa, M., Itsumi, M., Funatsu, T., Sakurai, A., Shintani, S., Kato, H., Fujita, T., Maruoka, Y., and Kuwata, H. (2022). Melatonin suppresses the antiviral immune response to EMCV infection through intracellular ATP deprivation caused by mitochondrial fragmentation. Heliyon 8, e11149. ♦
Emralino, F.L., Satoh, S., Sakai, N., Takami, M., Takeuchi, F., Yan, N., Rutsch, F., Fujita, T., and Kato, H. (2022). Double-Stranded RNA Induces Mortality in an MDA5-Mediated Type I Interferonopathy Model. Journal of immunology (Baltimore, Md. : 1950). ♦
Russ, A., Wittmann, S., Tsukamoto, Y., Herrmann, A., Deutschmann, J., Lagisquet, J., Ensser, A., Kato, H., and Gramberg, T. (2022). Nsp16 shields SARS-CoV-2 from efficient MDA5 sensing and IFIT1-mediated restriction. EMBO reports, e55648. ♦
Lee, S., Hirota, K., Schuette, V., Fujita, T., and Kato, H. (2022). Attenuation of regulatory T cell function by type I IFN signaling in an MDA5 gain-of-function mutant mouse model. Biochemical and biophysical research communications 629, 171-175. ♦
Zuo, W., Wakimoto, M., Kozaiwa, N., Shirasaka, Y., Oh, S.-W., Fujiwara, S., Miyachi, H., Kogure, A., Kato, H., and Fujita, T. (2022). PKR and TLR3 trigger distinct signals that coordinate the induction of antiviral apoptosis. Cell Death Dis 13. ♦
Karagiannis, F., Peukert, K., Surace, L., Michla, M., Nikolka, F., Fox, M., Weiss, P., Feuerborn, C., Maier, P., Schulz, S., Al, B., Seeliger, B., Welte, T., David, S., Grondman, I., Nooijer, A.H. de, Pickkers, P., Kleiner, J.L., Berger, M.M., Brenner, T., Putensen, C., Kato, H., Garbi, N., Netea, M.G., Hiller, K., Placek, K., Bode, C., and Wilhelm, C. (2022). Impaired ketogenesis ties metabolism to T cell dysfunction in COVID-19. Nature. ♦
Bergant, V., Yamada, S., Grass, V., Tsukamoto, Y., Lavacca, T., Krey, K., Mühlhofer, M.-T., Wittmann, S., Ensser, A., Herrmann, A., vom Hemdt, A., Tomita, Y., Matsuyama, S., Hirokawa, T., Huang, Y., Piras, A., Jakwerth, C.A., Oelsner, M., Thieme, S., Graf, A., Krebs, S., Blum, H., Kümmerer, B.M., Stukalov, A., Schmidt-Weber, C.B., Igarashi, M., Gramberg, T., Pichlmair, A., and Kato, H. (2022). Attenuation of SARS-CoV-2 replication and associated inflammation by concomitant targeting of viral and host cap 2'-O-ribose methyltransferases. The EMBO journal, e111608. ♦
Saikruang, W., Ang Yan Ping, L., Abe, H., Kasumba, D.M., Kato, H., and Fujita, T. (2022). The RNA helicase DDX3 promotes IFNB transcription via enhancing IRF-3/p300 holocomplex binding to the IFNB promoter. Scientific reports 12, 3967. ♦
Marx, S., Kümmerer, B.M., Grützner, C., Kato, H., Schlee, M., Renn, M., Bartok, E., and Hartmann, G. (2022). RIG-I-induced innate antiviral immunity protects mice from lethal SARS-CoV-2 infection. Molecular therapy. Nucleic acids 27, 1225-1234. ♦
Ohto, T., Tayeh, A.A., Nishikomori, R., Abe, H., Hashimoto, K., Baba, S., Arias-Loza, A.-P., Soda, N., Satoh, S., Matsuda, M., Iizuka, Y., Kondo, T., Koseki, H., Yan, N., Higuchi, T., Fujita, T., and Kato, H. (2022). Intracellular virus sensor MDA5 mutation develops autoimmune myocarditis and nephritis. Journal of autoimmunity 127, 102794. ♦
Hayashi, Y., Suzuki, H., Nakajima, W., Uehara, I., Tanimura, A., Himeda, T., Koike, S., Katsuno, T., Kitajiri, S.-I., Koyanagi, N., Kawaguchi, Y., Onomoto, K., Kato, H., Yoneyama, M., Fujita, T., and Tanaka, N. (2021). Virus-infection in cochlear supporting cells induces audiosensory receptor hair cell death by TRAIL-induced necroptosis. PloS one 16, e0260443. ♦
Koenig, P.-A., Das, H., Liu, H., Kümmerer, B.M., Gohr, F.N., Jenster, L.-M., Schiffelers, L.D.J., Tesfamariam, Y.M., Uchima, M., Wuerth, J.D., Gatterdam, K., Ruetalo, N., Christensen, M.H., Fandrey, C.I., Normann, S., Tödtmann, J.M.P., Pritzl, S., Hanke, L., Boos, J., Yuan, M., Zhu, X., Schmid-Burgk, J.L., Kato, H., Schindler, M., Wilson, I.A., Geyer, M., Ludwig, K.U., Hällberg, B.M., Wu, N.C., and Schmidt, F.I. (2021). Structure-guided multivalent nanobodies block SARS-CoV-2 infection and suppress mutational escape. Science (New York, N.Y.). ♦
Khalil, J., Kato, H., Fujita, T., 2021. The Role of Non-Structural Protein NSs in the Pathogenesis of Severe Fever with Thrombocytopenia Syndrome. Viruses 13. ♦
Onizawa, H., Kato, H., Kimura, H., Kudo, T., Soda, N., Shimizu, S., Funabiki, M., Yagi, Y., Nakamoto, Y., Priller, J., Nishikomori, R., Heike, T., Yan, N., Tsujimura, T., Mimori, T., Fujita, T., 2020. Aicardi-Goutières syndrome-like encephalitis in mutant mice with constitutively active MDA5. International immunology. ♦
Abu Tayeh, A., Funabiki, M., Shimizu, S., Satoh, S., Sumin, L., Iwakura, Y., Kato, H., Fujita, T., 2020. Psoriasis-like skin disorder in transgenic mice expressing a RIG-I Singleton-Merten syndrome variant. International immunology. ♦
Abe, H., Satoh, J., Shirasaka, Y., Kogure, A., Kato, H., Ito, S., Fujita, T. 2020. Priming Phosphorylation of TANK-Binding Kinase 1 by IkappaB Kinase beta Is Essential in Toll-Like Receptor 3/4 Signaling. Molecular and cellular biology 40 (5). ♦
Akahori, Y., Kato, H., Fujita, T., Moriishi, K., Tanaka, Y., Watashi, K., Imamura, M., Chayama, K., Wakita, T., Hijikata, M. 2020. Establishment of a novel hepatitis B virus culture system using immortalized human hepatocytes. Scientific reports 10, 21718. ♦
Duic, I., Tadakuma, H., Harada, Y., Yamaue, R., Deguchi, K., Suzuki, Y., Yoshimura, S.H., Kato, H., Takeyasu, K., Fujita, T., 2020. Viral RNA recognition by LGP2 and MDA5, and activation of signaling through step-by-step conformational changes. Nucleic acids research. ♦
Hayashi, Y., Suzuki, H., Nakajima, W., Uehara, I., Tanimura, A., Himeda, T., Koike, S., Katsuno, T., Kitajiri, S.-I., Koyanagi, N., Kawaguchi, Y., Onomoto, K., Kato, H., Yoneyama, M., Fujita, T., Tanaka, N., 2020. Cochlear supporting cells function as macrophage-like cells and protect audiosensory receptor hair cells from pathogens. Scientific reports 10 (1), 6740. ♦
Khalil, J., Yamada, S., Tsukamoto, Y., Abe, H., Shimojima, M., Kato, H., Fujita, T., 2020. The Non-structural Protein NSs of SFTSV Causes Cytokine Storm Through the Hyper-activation of NF-kappaB. Molecular and Cellular Biology. ♦
Sha, T.W., Weber, M., Kasumba, D.M., Noda, T., Nakano, M., Kato, H., Fujita, T., 2020. Influenza A virus NS1 optimises virus infectivity by enhancing genome packaging in a dsRNA-binding dependent manner. Virology journal 17 (1), 107. ♦
Hajake, T., Matsuno, K., Kasumba, D.M., Oda, H., Kobayashi, M., Miyata, N., Shinji, M., Kogure, A., Kasajima, N., Okamatsu, M., Sakoda, Y., Kato, H., Fujita, T., 2019. Broad and systemic immune-modulating capacity of plant-derived dsRNA. International immunology 31 (12), 811–821. ♦
Ng, C.S., Kato, H., Fujita, T., 2019. Fueling Type I Interferonopathies: Regulation and Function of Type I Interferon Antiviral Responses. Journal of interferon & cytokine research : the official journal of the International Society for Interferon and Cytokine Research 39 (7), 383–392. ♦
Soda, N., Sakai, N., Kato, H., Takami, M., Fujita, T., 2019. Singleton-Merten Syndrome-like Skeletal Abnormalities in Mice with Constitutively Activated MDA5. Journal of immunology (Baltimore, Md. : 1950) 203 (5), 1356–1368. ♦
Takahasi, K., Onomoto, K., Horiuchi, M., Kato, H., Fujita, T., Yoneyama, M., 2019. Identification of a new autoinhibitory domain of interferon-beta promoter stimulator-1 (IPS-1) for the tight regulation of oligomerization-driven signal activation. Biochemical and biophysical research communications 517 (4), 662–669. ♦
Takeuchi, F., Ikeda, S., Tsukamoto, Y., Iwasawa, Y., Qihao, C., Otakaki, Y., Ryota, O., Yao, W.-L., Narita, R., Makoto, H., Watashi, K., Wakita, T., Takeuchi, K., Chayama, K., Kogure, A., Kato, H., Fujita, T., 2019. Screening for inhibitor of episomal DNA identified dicumarol as a hepatitis B virus inhibitor. PloS one 14 (2), e0212233. ♦
Yamada, S., Shimojima, M., Narita, R., Tsukamoto, Y., Kato, H., Saijo, M., Fujita, T. 2018. RIG-I-Like Receptor and Toll-Like Receptor Signaling Pathways Cause Aberrant Production of Inflammatory Cytokines/Chemokines in a Severe Fever with Thrombocytopenia Syndrome Virus Infection Mouse Model. Journal of virology 92. ♦
Tsukamoto, Y., Ikeda, S., Uwai, K., Taguchi, R., Chayama, K., Sakaguchi, T., Narita, R., Yao, W.-L., Takeuchi, F., Otakaki, Y., et al. 2018. Rosmarinic acid is a novel inhibitor for Hepatitis B virus replication targeting viral epsilon RNA-polymerase interaction. PloS one 13, e0197664. ♦
Kasumba, D.M., Hajake, T., Oh, S.-W., Kotenko, S.V., Kato, H., Fujita, T. 2017. A Plant-Derived Nucleic Acid Reconciles Type I IFN and a Pyroptotic-like Event in Immunity against Respiratory Viruses. Journal of immunology (Baltimore, Md. : 1950) 199, 2460-2474. ♦
Kato, H., Oh, S.-W., Fujita, T. 2017. RIG-I-Like Receptors and Type I Interferonopathies. Journal of interferon & cytokine research : the official journal of the International Society for Interferon and Cytokine Research 37, 207-213. ♦
Yao, W.-L., Ikeda, S., Tsukamoto, Y., Shindo, K., Otakaki, Y., Qin, M., Iwasawa, Y., Takeuchi, F., Kaname, Y., Chou, Y.-C., et al. 2017. Establishment of a human hepatocellular cell line capable of maintaining long-term replication of hepatitis B virus. International immunology 29, 109-120. ♦
Oh, S.-W., Onomoto, K., Wakimoto, M., Onoguchi, K., Ishidate, F., Fujiwara, T., Yoneyama, M., Kato, H., Fujita, T. 2016. Leader-Containing Uncapped Viral Transcript Activates RIG-I in Antiviral Stress Granules. PLoS pathogens 12, e1005444. ♦
Kato, H., Fujita, T. 2015. RIG-I-like receptors and autoimmune diseases. Curr Opin Immunol 37, 40-45. ♦
Narita, R., Takahasi, K., Murakami, E., Hirano, E., Yamamoto, S.P., Yoneyama, M., Kato, H., Fujita, T. 2014. A novel function of human Pumilio proteins in cytoplasmic sensing of viral infection. PLoS pathogens 10, e1004417. ♦
Funabiki, M.°, Kato, H.°, Miyachi, Y., Toki, H., Motegi, H., Inoue, M., Minowa, O., Yoshida, A., Deguchi, K., Sato, H., Ito, S., Shiroishi, T., Takeyasu, K., Noda, T., Fujita, T. 2014. Autoimmune disorders associated with gain of function of the intracellular sensor MDA5. Immunity 40, 199-212. °equal contribution ♦
Kato, H., Fujita, T. 2014. Autoimmunity caused by constitutive activation of cytoplasmic viral RNA sensors. Cytokine & growth factor reviews 25, 739-743. ♦
Oda, H., Nakagawa, K., Abe, J., Awaya, T., Funabiki, M., Hijikata, A., Nishikomori, R., Funatsuka, M., Ohshima, Y., Sugawara, Y., Yasumi, T., Kato, H., Shirai, T., Ohara, O., Fujita, T., Heike, T. 2014. Aicardi-Goutieres syndrome is caused by IFIH1 mutations. Am J Hum Genet 95, 121-125. ♦
Onomoto, K., Yoneyama, M., Fung, G., Kato, H., Fujita, T. 2014. Antiviral innate immunity and stress granule responses. Trends in immunology 35, 420-428. ♦
Yoo, J.-S., Kato, H., Fujita, T. 2014. Sensing viral invasion by RIG-I like receptors. Current opinion in microbiology 20, 131-138. ♦
Yoo, J.-S., Takahasi, K., Ng, C.S., Ouda, R., Onomoto, K., Yoneyama, M., Lai, J.C., Lattmann, S., Nagamine, Y., Matsui, T., et al. 2014b. DHX36 enhances RIG-I signaling by facilitating PKR-mediated antiviral stress granule formation. PLoS pathogens 10, e1004012. ♦
Tsugawa, Y., Kato, H., Fujita, T., Shimotohno, K., Hijikata, M. 2014. Critical role of interferon-alpha constitutively produced in human hepatocytes in response to RNA virus infection. PloS one 9, e89869. ♦
Ori, D., Kato, H., Sanjo, H., Tartey, S., Mino, T., Akira, S., Takeuchi, O. 2013. Essential roles of K63-linked polyubiquitin-binding proteins TAB2 and TAB3 in B cell activation via MAPKs. Journal of immunology (Baltimore, Md.: 1950) 190, 4037-4045. ♦
Ng, C.S., Jogi, M., Yoo, J.-S., Onomoto, K., Koike, S., Iwasaki, T., Yoneyama, M., Kato, H., Fujita, T. 2013. Encephalomyocarditis virus disrupts stress granules, the critical platform for triggering antiviral innate immune responses. Journal of virology 87, 9511-9522. ♦
Hayashi, Y., Onomoto, K., Narita, R., Yoneyama, M., Kato, H., Nakagawa, T., Ito, J., Taura, A., Fujita, T. 2013. Virus-induced expression of retinoic acid inducible gene-I and melanoma differentiation-associated gene 5 in the cochlear sensory epithelium. Microbes and infection 15, 592-598. ♦
Takamatsu, S., Onoguchi, K., Onomoto, K., Narita, R., Takahasi, K., Ishidate, F., Fujiwara, T.K., Yoneyama, M., Kato, H., Fujita, T. 2013. Functional characterization of domains of IPS-1 using an inducible oligomerization system. PloS one 8, e53578. ♦
Ng, C.S., Kato, H., Fujita, T. 2012. Recognition of viruses in the cytoplasm by RLRs and other helicases-how conformational changes, mitochondrial dynamics and ubiquitination control innate immune responses. International immunology 24, 739-749. ♦
Kageyama, M., Takahasi, K., Narita, R., Hirai, R., Yoneyama, M., Kato, H., Fujita, T. 2011. 55 Amino acid linker between helicase and carboxyl terminal domains of RIG-I functions as a critical repression domain and determines inter-domain conformation. Biochemical and biophysical research communications 415, 75-81. ♦
Kato, H., Takahasi, K., Fujita, T. 2011. RIG-I-like receptors: cytoplasmic sensors for non-self RNA. Immunological reviews 243, 91-98. ♦
Ouda, R., Onomoto, K., Takahasi, K., Edwards, M.R., Kato, H., Yoneyama, M., Fujita, T. 2011. Retinoic acid-inducible gene I-inducible miR-23b inhibits infections by minor group rhinoviruses through down-regulation of the very low density lipoprotein receptor. The Journal of biological chemistry 286, 26210-26219. ♦
Miyake, T., Satoh, T., Kato, H., Matsushita, K., Kumagai, Y., Vandenbon, A., Tani, T., Muta, T., Akira, S., Takeuchi, O. 2010. IkappaBzeta is essential for natural killer cell activation in response to IL-12 and IL-18. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America 107, 17680-17685. ♦
Schulz, O., Pichlmair, A., Rehwinkel, J., Rogers, N.C., Scheuner, D., Kato, H., Takeuchi, O., Akira, S., Kaufman, R.J., Reis e Sousa, C. 2010. Protein kinase R contributes to immunity against specific viruses by regulating interferon mRNA integrity. Cell host & microbe 7, 354-361. ♦
Satoh, T., Kato, H., Kumagai, Y., Yoneyama, M., Sato, S., Matsushita, K., Tsujimura, T., Fujita, T., Akira, S., Takeuchi, O. 2010. LGP2 is a positive regulator of RIG-I- and MDA5-mediated antiviral responses. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the Uinted States of America 107, 1512-1517. °equal contribution ♦
Poeck, H., Bscheider, M., Gross, O., Finger, K., Roth, S., Rebsamen, M., Hannesschlager, N., Schlee, M., Rothenfusser, S., Barchet, W., et al. 2010. Recognition of RNA virus by RIG-I results in activation of CARD9 and inflammasome signaling for interleukin 1 beta production. Nature immunology 11, 63-69.
Schlee, M., Roth, A., Hornung, V., Hagmann, C.A., Wimmenauer, V., Barchet, W., Coch, C., Janke, M., Mihailovic, A., and Wardle, G., et al. (2009). Recognition of 5' triphosphate by RIG-I helicase requires short blunt double-stranded RNA as contained in panhandle of negative-strand virus. Immunity 31, 25-34. ♦
Papon, L., Oteiza, A., Imaizumi, T., Kato, H., Brocchi, E., Lawson, T.G., Akira, S., and Mechti, N. (2009). The viral RNA recognition sensor RIG-I is degraded during encephalomyocarditis virus (EMCV) infection. Virology 393, 311-318. ♦
Pichlmair, A., Schulz, O., Tan, C.-P., Rehwinkel, J., Kato, H., Takeuchi, O., Akira, S., Way, M., Schiavo, G., Reis e Sousa, C. 2009. Activation of MDA5 requires higher-order RNA structures generated during virus infection. Journal of virology 83, 10761-10769. ♦
Kawagoe, T., Takeuchi, O., Takabatake, Y., Kato, H., Isaka, Y., Tsujimura, T., and Akira, S. (2009). TANK is a negative regulator of Toll-like receptor signaling and is critical for the prevention of autoimmune nephritis. Nature immunology 10, 965-972. ♦
Matsushita, K., Takeuchi, O., Standley, D.M., Kumagai, Y., Kawagoe, T., Miyake, T., Satoh, T., Kato, H., Tsujimura, T., Nakamura, H., et al. 2009. Zc3h12a is an RNase essential for controlling immune responses by regulating mRNA decay. Nature 458, 1185-1190. ♦
Rasmussen, S.B., Jensen, S.B., Nielsen, C., Quartin, E., Kato, H., Chen, Z.J., Silverman, R.H., Akira, S., and Paludan, S.R. (2009). Herpes simplex virus infection is sensed by both Toll-like receptors and retinoic acid-inducible gene- like receptors, which synergize to induce type I interferon production. The Journal of general virology 90, 74-78. ♦
Kato, H., Takeuchi, O., Mikamo-Satoh, E., Hirai, R., Kawai, T., Matsushita, K., Hiiragi, A.,Dermody, T.S., Fujita, T., Akira, S. 2008. Length-dependent recognition of double-stranded ribonucleic acids by retinoic acid-inducible gene-I and melanoma differentiation-associated gene 5. J Exp Med 205, 1601-1610. ♦
Jung, A., Kato, H., Kumagai, Y., Kumar, H., Kawai, T., Takeuchi, O., Akira, S. 2008. Lymphocytoid choriomeningitis virus activates plasmacytoid dendritic cells and induces a cytotoxic T-cell response via MyD88. Journal of virology 82, 196-206. ♦
Poeck, H., Besch, R., Maihoefer, C., Renn, M., Tormo, D., Morskaya, S.S., Kirschnek, S., Gaffal, E., Landsberg, J., Hellmuth, J., et al. 2008. 5'-Triphosphate-siRNA: turning gene silencing and Rig-I activation against melanoma. Nature medicine 14, 1256-1263. ♦
Karikó, K., Muramatsu, H., Welsh, F.A., Ludwig, J., Kato, H., Akira, S., Weissman, D. 2008. Incorporation of pseudouridine into mRNA yields superior nonimmunogenic vector with increased translational capacity and biological stability. Molecular therapy : the journal of the American Society of Gene Therapy 16, 1833-1840. ♦
Kawagoe, T., Sato, S., Jung, A., Yamamoto, M., Matsui, K., Kato, H., Uematsu, S., Takeuchi, O., Akira, S. 2007. Essential role of IRAK-4 protein and its kinase activity in Toll-like receptor-mediated immune responses but not in TCR signaling. The Journal of experimental medicine 204, 1013-1024. ♦
Kumagai, Y., Takeuchi, O., Kato, H., Kumar, H., Matsui, K., Morii, E., Aozasa, K., Kawai, T., Akira, S. 2007. Alveolar macrophages are the primary interferon-alpha producer in pulmonary infection with RNA viruses. Immunity 27, 240-252. ♦
Roberts, Z.J., Goutagny, N., Perera, P.-Y., Kato, H., Kumar, H., Kawai, T., Akira, S., Savan, R., van Echo, D., Fitzgerald, K.A., et al. 2007. The chemotherapeutic agent DMXAA potently and specifically activates the TBK1-IRF-3 signaling axis. The Journal of experimental medicine 204, 1559-1569. ♦
Hornung, V., Ellegast, J., Kim, S., Brzozka, K., Jung, A., Kato, H., Poeck, H., Akira, S., Conzelmann, K.K., Schlee, M., Endres, S., Hartmann, G. 2006. 5’-Triphosphate RNA is the ligand for RIG-I. Science 314, 994-997. ♦
Ishii, K.J., Coban, C., Kato, H., Takahashi, K., Torii, Y., Takeshita, F., Ludwig, H., Sutter, G., Suzuki, K., and Hemmi, H., et al. (2006). A Toll-like receptor-independent antiviral response induced by double-stranded B-form DNA. Nature immunology 7, 40-48. ♦
Kato, H., Takeuchi, O., Sato, S., Yoneyama, M., Yamamoto, M., Matsui, K., Uematsu, S., Jung, A., Kawai, T., Ishii, K.J., Yamaguchi, O., Otsu, K., Tsujimura, T., Koh, C.S., Reis e Sousa, C., Matsuura, Y., Fujita, T., and Akira, S. (2006). Differential roles of MDA5 and RIG-I helicases in the recognition of RNA viruses. Nature 441, 101-105. ♦
Kumar, H., Kawai, T., Kato, H., Sato, S., Takahashi, K., Coban, C., Yamamoto, M., Uematsu, S., Ishii, K.J., Takeuchi, O., Akira, S. 2006. Essential role of IPS-1 in innate immune responses against RNA viruses. The Journal of Experimental Medicine 203, 1795-1803. ♦
Matsui, K., Kumagai, Y., Kato, H., Sato, S., Kawagoe, T., Uematsu, S., Takeuchi, O., Akira, S. 2006. Cutting edge: Role of TANK-binding kinase 1 and inducible IkappaB kinase in IFN responses against viruses in innate immune cells. Journal of immunology (Baltimore, Md. : 1950) 177, 5785-5789. ♦
Uematsu, S., Jang, M.H., Chevrier, N., Guo, Z., Kumagai, Y., Yamamoto, M., Kato, H., Sougawa, N., Matsui, H., Kuwata, H., Hemmi, H., Coban, C., Kawai, T., Ishii, K.J., Takeuchi, O., Miyasaka, M., Takeda, K., Akira, S. 2006. Detection of pathogenic intestinal bacteria by Toll-like receptor 5 on intestinal CD11c+ lamina propria cells. Nature immunology 7, 868-874. ♦
Uematsu, S., Sato, S., Yamamoto, M., Hirotani, T., Kato, H., Takeshita, F., Matsuda, M., Coban, C., Ishii, K.J., Kawai, T., Takeuchi, O., and Akira, S. (2005). Interleukin-1 receptor-associated kinase-1 plays an essential role for Toll-like receptor (TLR)7- and TLR9-mediated interferon-{alpha} induction. The Journal of experimental medicine 201, 915-923. ♦
Kawai, T., Takahashi, K., Sato, S., Coban, C., Kumar, H., Kato, H., Ishii, K.J., Takeuchi, O., Akira, S. 2005. IPS-1, an adaptor triggering RIG-I- and Mda5-mediated type I interferon induction. Nat Immunol 6, 981-988. ♦
Kato, H., Sato, S., Yoneyama, M., Yamamoto, M., Uematsu, S., Matsui, K., Tsujimura, T., Takeda, K., Fujita, T., Takeuchi, O., Akira, S. 2005. Cell type-specific involvement of RIG-I in antiviral response. Immunity 23, 19-28. ♦
















